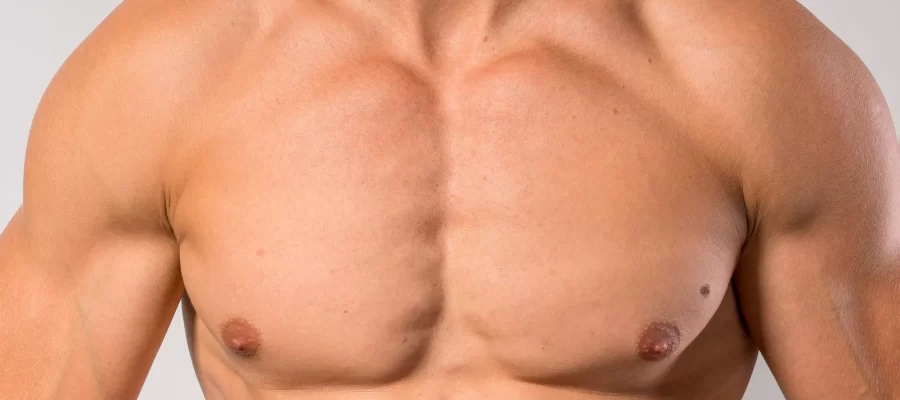
What Is Gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia is a condition in men that causes the breast tissue to enlarge, creating the appearance of feminine-like breasts. This is not simply an accumulation of fat, but rather the growth of glandular tissue beneath the nipple and areola area. The condition can occur at any age, from adolescence to adulthood, and often affects one or both sides of the chest. While gynecomastia itself is not life-threatening, it can cause emotional distress, social discomfort, and self-confidence issues in men. Many patients seek medical advice or treatment not only for aesthetic reasons but also for psychological relief.
What Causes Gynecomastia in Men?
The main cause of gynecomastia is an imbalance between the hormones estrogen and testosterone. When estrogen levels rise or testosterone levels decrease, the glandular breast tissue may begin to grow. This hormonal imbalance can be triggered by several factors such as puberty, aging, certain medications, or underlying health conditions. Teenagers may experience temporary gynecomastia due to puberty changes, and in most cases, the tissue reduces naturally after a few months or years.
In adult men, the condition may be linked to lifestyle factors such as alcohol consumption, anabolic steroids, and some drugs used for heart disease, ulcers, or psychiatric disorders. Medical conditions like liver disease, kidney failure, or hormonal disorders can also play a role. In addition, obesity may worsen the appearance of gynecomastia since excess fat increases estrogen production, which further affects the hormonal balance.
Who Is a Suitable Candidate for Gynecomastia Surgery?
Not every patient requires surgery, but men who suffer from persistent gynecomastia that does not resolve with time or non-surgical measures may consider surgical treatment. A suitable candidate is generally in good overall health, has stable body weight, and experiences discomfort or emotional distress due to the enlarged breast tissue. Candidates should also have realistic expectations about the outcomes of surgery.
Surgical intervention is often considered when the breast tissue is firm, fibrous, or glandular, making it resistant to diet or exercise. Men who feel limited in their choice of clothing, avoid social activities such as swimming, or suffer from reduced self-esteem often find significant relief after treatment. It is also important that candidates do not have untreated hormonal disorders or health conditions that could complicate healing.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Gynecomastia
The most common symptom of gynecomastia is a noticeable enlargement of one or both breasts in men. This enlargement usually feels firm rather than soft and is located directly under the nipple. In some cases, the condition may be painful or sensitive to touch, though many men experience no discomfort beyond the visual change.
Diagnosis is usually made through a physical examination, where the doctor evaluates the size and consistency of the breast tissue. Sometimes additional tests such as blood analysis, mammograms, or ultrasounds may be required to rule out other conditions such as tumors or hormonal imbalances. Understanding the underlying cause is essential for determining the best treatment plan, whether surgical or non-surgical.
How Is Gynecomastia Surgery Performed?
Gynecomastia surgery, also known as male breast reduction, aims to remove the excess glandular tissue, fat, and sometimes skin to restore a flatter and more masculine chest contour. The procedure is typically carried out under general or local anesthesia with sedation.
Depending on the severity, different surgical techniques may be used. For patients with mostly fatty tissue, liposuction may be sufficient to reduce the size. In cases where glandular tissue is more prominent, an excision technique is required. This involves making small incisions around the areola or under the chest fold to remove the glandular tissue directly. In more severe cases, a combination of liposuction and excision may be necessary.
After surgery, patients usually wear a compression garment to reduce swelling and support the chest during healing. Recovery times vary but most men can return to work within one week and resume exercise after a few weeks. The scars from gynecomastia surgery are typically small and well-hidden, becoming less noticeable over time.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options for Gynecomastia
Not every case of gynecomastia requires surgery. For adolescents and men experiencing mild symptoms, observation and lifestyle changes may be enough, as the condition often improves naturally. Weight loss and exercise can reduce the appearance of gynecomastia if excess fat contributes to the condition, although this will not eliminate glandular tissue.
Hormonal treatments may be considered if the condition is caused by a clear hormonal imbalance. Adjusting or discontinuing medications that trigger gynecomastia may also help resolve the problem. In some cases, doctors recommend specific drug therapies that block estrogen effects or increase testosterone levels, although these are less commonly used and depend on the patient’s overall health.
What to Expect Before and After Gynecomastia Surgery
Before gynecomastia surgery, patients typically undergo a detailed medical evaluation to determine the cause of breast tissue enlargement and to ensure overall health is suitable for the procedure. This includes physical examination, blood tests, and in some cases imaging scans to assess the glandular and fatty components of the chest. In preparation for surgery, lifestyle adjustments such as quitting smoking and avoiding certain medications may be advised, as these can interfere with healing.
After the operation, patients can expect some swelling, mild bruising, and sensitivity in the treated area. A compression garment is usually worn to minimize swelling and support the chest shape during the recovery phase. While the initial results are visible immediately, final outcomes take several weeks as swelling subsides and tissues settle.
Recovery Process After Male Breast Reduction
Recovery after gynecomastia surgery is generally smooth, with most men resuming normal activities within one week. Light physical activity is encouraged early, but heavy exercise and weightlifting are usually postponed for about four to six weeks. Pain is typically mild to moderate and controlled with prescribed medication.
During the first few days, rest is important, but movement should not be completely restricted to avoid stiffness. Stitches are often removed within one to two weeks, depending on the technique used. The majority of patients report a significant boost in self-confidence and improved body image after healing is complete. Long-term results are stable as long as body weight and hormone levels remain consistent.
Risks and Side Effects of Gynecomastia Treatment
While gynecomastia surgery is considered safe, it carries some risks and potential side effects like any surgical procedure. Common side effects include temporary swelling, bruising, and numbness in the chest area. These usually resolve within a few weeks.
More rare complications may include infection, bleeding, noticeable scarring, or asymmetry between the two sides of the chest. In some cases, changes in nipple sensation may occur, which can be temporary or permanent. Following all post-operative care instructions significantly reduces these risks. Choosing an experienced surgeon also plays a vital role in minimizing complications.
Tips for Preventing Gynecomastia Recurrence
Preventing gynecomastia recurrence involves addressing the root causes. Maintaining a stable weight, adopting a balanced diet, and avoiding anabolic steroids or drugs known to affect hormone levels are essential steps. Moderating alcohol consumption and monitoring medications that influence estrogen or testosterone can also be important in prevention.
Regular check-ups help detect hormonal imbalances early, allowing timely intervention. For men with underlying medical conditions, proper management of liver, kidney, or thyroid problems lowers the likelihood of recurrence. A healthy lifestyle combined with ongoing medical monitoring helps ensure long-lasting surgical results.
Gynecomastia Prices 2025
The cost of gynecomastia surgery in 2025 varies depending on the severity of the condition, the techniques used, and whether liposuction or excision—or a combination of both—is required. Prices also change according to the location, the medical team’s expertise, and the type of anesthesia.
In Turkey, gynecomastia surgery prices are generally more affordable compared to many other countries while maintaining high medical standards. The overall fee often includes consultation, surgery, anesthesia, and follow-up visits. Patients should always prioritize safety and surgical expertise over cost alone, ensuring long-term satisfaction and minimized risks.
Is Gynecomastia Permanent?
Gynecomastia is the enlargement of male breast tissue, often caused by hormonal imbalance, certain medications, or lifestyle factors. In some men, the condition may improve over time, especially if the cause is temporary, such as puberty or medication use. However, when glandular tissue develops fully, it does not usually shrink on its own, even if weight loss reduces fat in the chest. This means that in many cases gynecomastia becomes a long-term or permanent condition. The stability of the condition depends on whether the hormonal balance remains consistent and whether external triggers continue to affect the body. For men seeking lasting change in chest appearance, surgery is often considered the most effective solution.
Can Gynecomastia Go Away Without Surgery?
There are cases where gynecomastia resolves naturally without surgical treatment. During puberty, many adolescents experience temporary breast enlargement due to hormonal fluctuations. In most cases, this condition disappears within six months to two years as hormone levels stabilize. For adults, stopping the use of certain drugs or substances that influence hormone balance—such as anabolic steroids, alcohol, or specific medications—can sometimes lead to improvement. Additionally, losing excess body weight may reduce the fatty component of gynecomastia but not the glandular tissue. Because true glandular enlargement does not regress with exercise or diet, surgery remains the only definitive treatment when the condition persists.
Is the Surgery Painful?
Male breast reduction surgery for gynecomastia is typically performed under general or local anesthesia with sedation, which ensures the procedure itself is painless. After surgery, patients can expect mild to moderate discomfort, especially during the first few days. This discomfort is usually managed effectively with prescribed pain medication. The majority of men describe the pain as manageable and similar to muscle soreness after intense exercise. Swelling and tightness in the chest area may also cause temporary discomfort. As healing progresses, pain decreases quickly, and most patients are able to move comfortably within a week.
How Long Does It Take to Heal After Male Breast Reduction?
Healing after gynecomastia surgery takes place in stages. Most men return to light daily activities within a week, though swelling and minor bruising may persist. By the second to third week, discomfort lessens significantly, and patients begin to see more natural chest contours. Exercise and heavy lifting are usually restricted for four to six weeks to prevent complications and allow tissues to recover fully. Complete healing, including scar maturation and final results, may take several months. Wearing a compression garment as recommended helps speed recovery and improves overall results. Patience during this period is important, as the body needs time to adapt to its new shape.
Will There Be Visible Scars After Surgery?
Scarring is an unavoidable part of any surgical procedure, but modern gynecomastia techniques aim to minimize their appearance. The type and location of scars depend on the surgical method used. If only liposuction is performed, tiny incisions are made, which usually fade over time and become barely noticeable. If glandular tissue removal is necessary, small incisions may be placed around the areola, where the natural color transition of the skin helps disguise them. With proper post-operative care, scars typically soften and fade within several months to a year. Factors such as skin type, genetics, and adherence to care instructions play a role in the final appearance of scars.